Egli Model
The Egli Model is a terrain model for radio frequency propagation. This model, which was first introduced by John Egli in his 1957 paper[1], was derived from real-world data on UHF and VHF television transmissions in several large cities. It predicts the total path loss for a point-to-point link. Typically used for outdoor line-of-sight transmission, this model provides the path loss as a single quantity.
Contents |
Applicable to/under conditions
The Egli model is typically suitable for cellular communication scenarios where one antenna is fixed and another is mobile. The model is applicable to scenarios where the transmission has to go over an irregular terrain. However, the model does not take into account travel through some vegetative obstruction, such as trees or shrubbery.
Coverage
Frequency: The model is typically applied to VHF and UHF spectrum transmissions.
Mathematical formulation
The Egli model is formally expressed as:
![L = G_B G_M \big[\frac{h_B h_M}{d^2}\big] ^2 [{\frac{40} {f}}]^2](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/8f5db9bc96e3c8299ab66b4727cebe50.png)
Where,
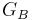 = Gain of the base station antenna. Unit: dimensionless
= Gain of the base station antenna. Unit: dimensionless
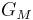 = Gain of the mobile station antenna. Unit: dimensionless
= Gain of the mobile station antenna. Unit: dimensionless
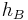 = Height of the base station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
= Height of the base station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
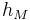 = Height of the mobile station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
= Height of the mobile station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
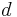 = Distance from base station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
= Distance from base station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
 = Frequency of transmission. Unit: megahertz (MHz)
= Frequency of transmission. Unit: megahertz (MHz)
Points to note
The equation is scaled for frequency specified in megahertz (MHz).
Limitations
This model predicts the path loss as a whole and does not subdivide the loss into free space loss and other losses.
Further reading
Introduction to RF propagation, John S. Seybold, 2005, John Willey and Sons Inc.
References
- ^ Egli, John J. (Oct. 1957). "Radio Propagation above 40 MC over Irregular Terrain". Proceedings of the IRE (IEEE) 45 (10): 1383–1391. doi:10.1109/JRPROC.1957.278224. ISSN 0096-8390.